The Kolumbo Volcanic Field, Greece: expert elicitation findings supporting volcanic hazard and risk assessment
Bevilacqua A., de’ Michieli Vitturi M., Tadini A., Neri A., Aspinall W.P., Sparks R.S.J. (2025).
Bulletin of Volcanology, 87(41). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-025-01822-3
Abstract
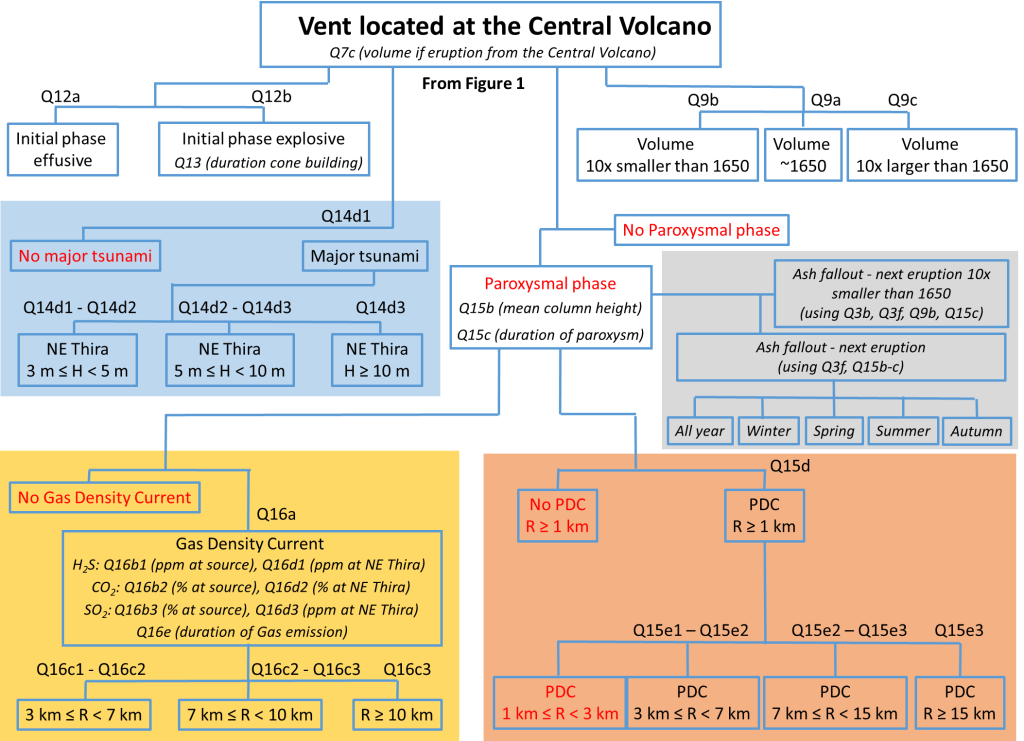
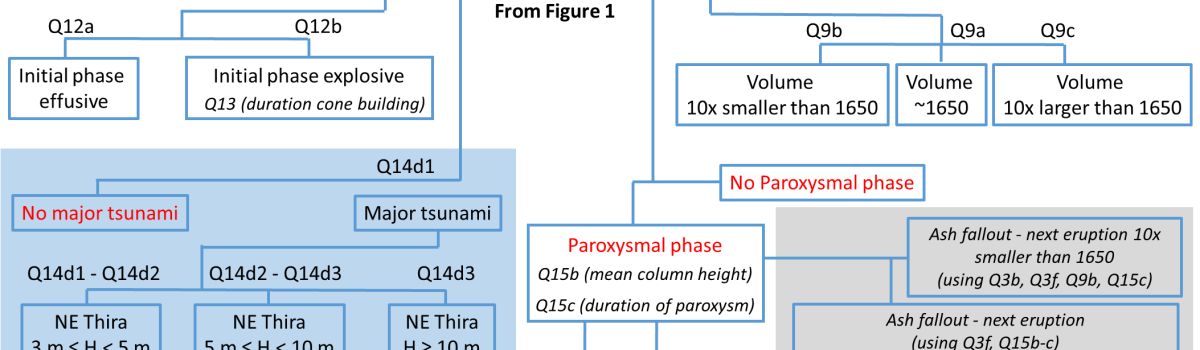
A detailed hazard and risk assessment has been undertaken for the Kolumbo Volcanic Field (KVF), which includes the Kulumbo Central Volcano, an active volcano situated in the Aegean Sea, Greece. In support, a comprehensive structured expert judgment exercise was conducted using the Classical Model for pooling specialists’ uncertainty quantifications concerning Target Item questions concerning volcanological model parameters, empirical variables, and event probabilities of interest. In total, 64 Target Items, organized according to a new event tree model for the KVF, were elicited from 15 specialists who participated in two workshops. Related statistical distributions and associated uncertainties were quantified via ELICIPY, a recently released Python tool implementing the Classical Model algorithm. The overarching methodological approach is summarized, and a number of examples of ELICIPY solutions for specific Target Items are given, illustrating the nature and key probabilistic features of such results. The Target Items included questions aimed at reconstructing the 1650 CE eruption of Kolumbo central Volcano and providing statistical characterizations as direct inputs to various hazard and risk models for a potential near-future eruption in the KVF. In addition, a new type of elicitation metric, the ‘Conformity Score’, is introduced in two alternative formulations for ranking the item-wise extents of agreement/disagreement between experts providing judgments; these rankings help inform stake holders which specific Target Items are well-constrained by expert elicitation, while also identifying where possible major knowledge gaps among experts may exist.


Devi effettuare l'accesso per postare un commento.