Accumulation and distribution of microplastics in coastal sediments from the inner Oslofjord, Norway
Bronzo L., A.L. Lusher, M. Schøyen, C. Morigi
Marine Pollution Bulletin, 173, Part B, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.113076
Abstract
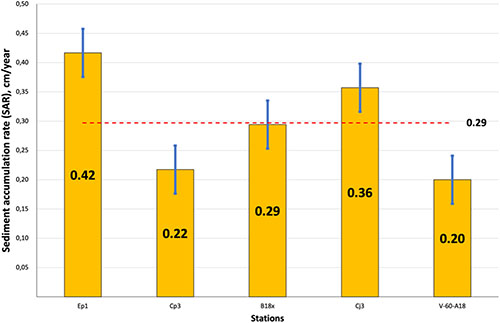
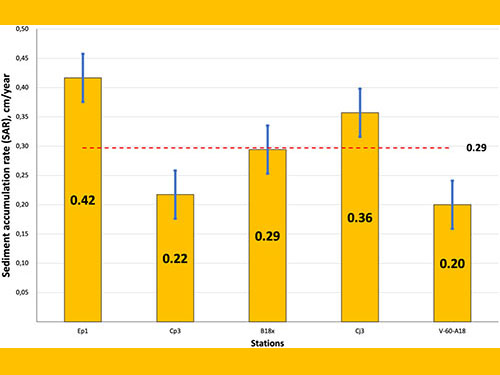
Microplastic presence in benthic marine systems is a widely discussed topic. The influence of the natural matrix on microplastic distribution within the sedimentary matrix is often overlooked. Marine sediments from the western inner Oslofjord, Norway, were investigated for temporal trends, with a particular focus on the relationship between sediment grain-sizes and microplastic distribution. Density separation, optical microscopy and chemical validation were used to categorize microplastics. Microplastic concentrations ranged from 0.02 to 1.71 MPs g − 1 dry weight (dw). Fibres were the most common (76%), followed by fragments and films (18%, 6%). Common polymers were polyesters (50%), polypropylene (18%), polymethylmethacrylate (9%), rayon and viscose (5%) and elastane (4%). Microplastics appear to accumulate preferentially according to their morphology and polymer type in certain sediment grain-sizes. Microplastics inputs to the Oslofjord appear to derive from a wastewater treatment plant in the vicinity. Although, the redistribution of microplastics within the fjord needs further investigation.


Devi effettuare l'accesso per postare un commento.