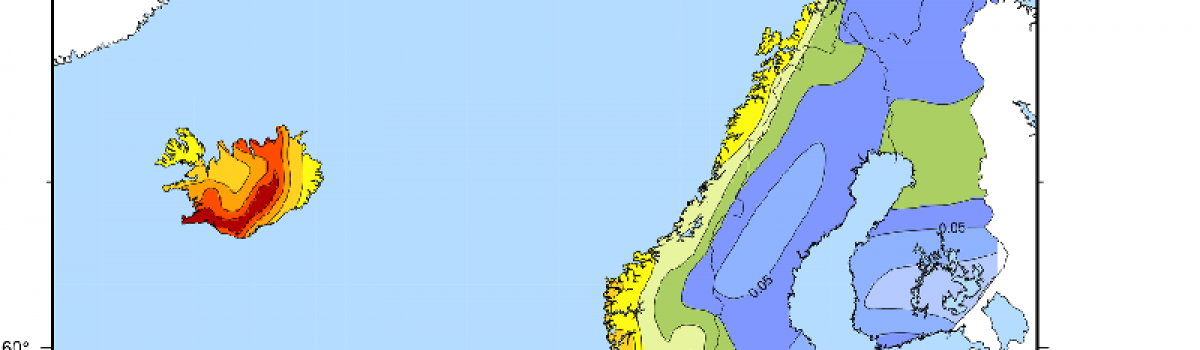
Gerstenberger M. C., W. Marzocchi, T. Allen, M. Pagani, J. Adams, L. Danciu, E. Field, H. Fujiwara, N. Luco, K-F Ma, C. Meletti, M. Petersen (2020).Review of Geophysics, doi:10.1029/2019RG000653. Si tratta di un lavoro di revisione nel quale viene descritto lo stato…
News
Tsunami and tephra deposits record interactions between past eruptive activity and landslides at Stromboli volcano, Italy
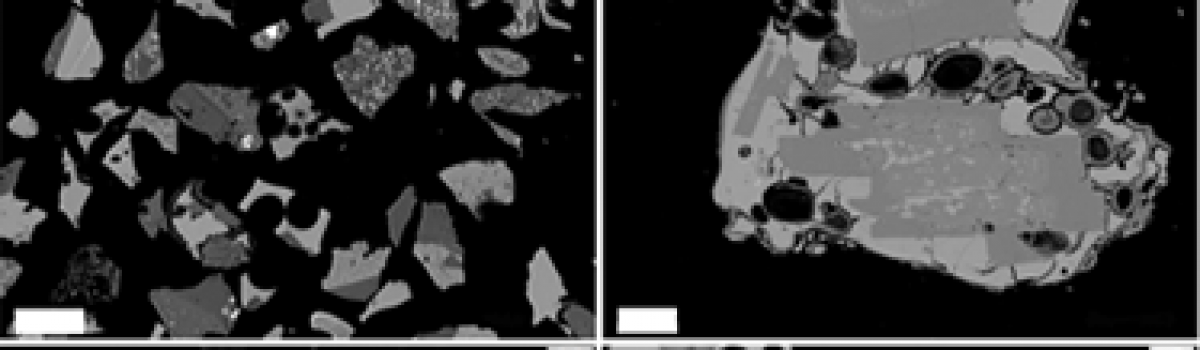
Figure 4. (A–D) Back-scattered mages showing variability of components in deposit T2a (lapilli-bearing ephra fallout sequence from Stromboli, Italy; juvenile scoriae and crystal fragments, holo-crystalline clasts, and scoriae with leached rims) (A); clast in T2a with milli-meter-thick rim of leached glass (B); juvenile, vesic-ular low-porphyritic (LP) pumice clast from T2a…
Catching Geomorphological Response to Volcanic Activity on Steep Slope Volcanoes Using Multi-Platform Remote Sensing
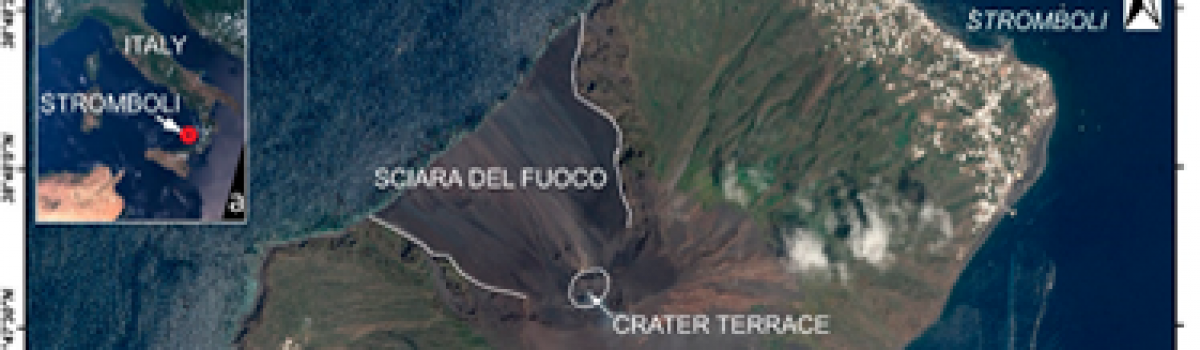
Geographic location of the Aeolian Islands (image collected by SENTINEL-3 on 19 July 2018); Di Traglia F., A. Fornaciai, M. Favalli, T. Nolesini, N. Casagli (2020).Remote Sensing, 12/3, 438; https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030438. Abstract The geomorphological evolution of the volcanic Island of Stromboli (Italy) between July 2010 and June…
Radial interpolation of GPS and leveling data of ground deformation in a resurgent caldera: application to Campi Flegrei (Italy)
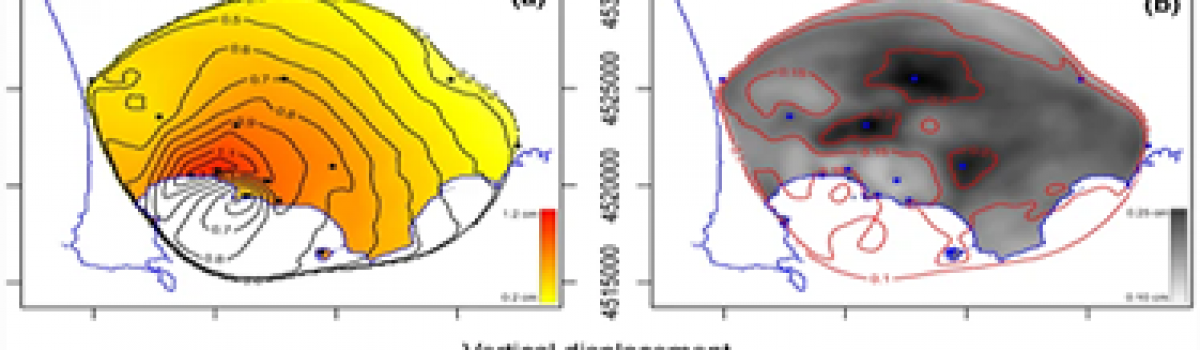
Plots a, c show the RIM interpolated maps of horizontal (a) and vertical (c) displacement, based on UP5 GPS data. Colors and contours are related to displacement values, in cm. Plots b, d show the related uncertainty ranges. Gray values and contours are related to displacement uncertainty values, in cm.
Numerical simulation of the tsunamis generated by the Sciara del Fuoco landslides (Stromboli Island, Italy)
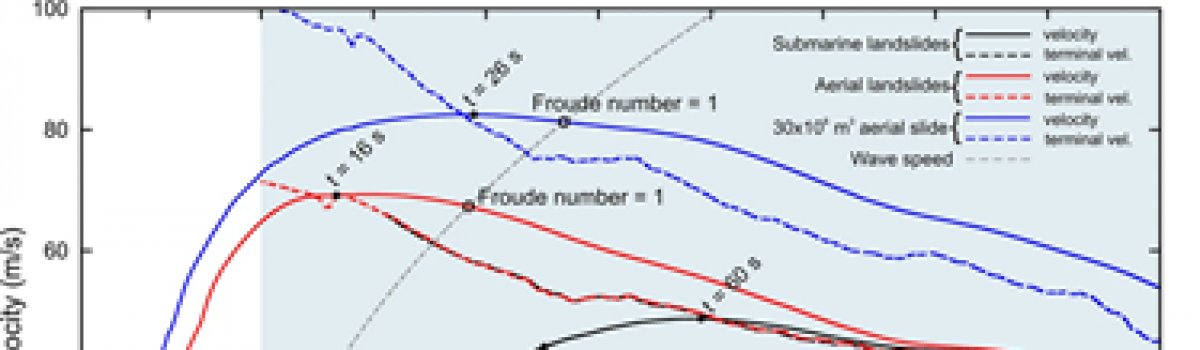
Velocity of the slides vs. depth. Terminal velocity and wave speed are also reported. Slides with same planimetric footprint have the same velocity. Fornaciai A., M. Favalli, L. Nannipieri (2019).Nature – Scientific Reports, 9.https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-54949-7#Abs1 Abstract Stromboli volcano (Aeolian Arc, Italy) experiences many mass failures along the…
Holocene Critical Zone dynamics in an Alpine catchment inferred from a speleothem multiproxy record: disentangling climate and human influences
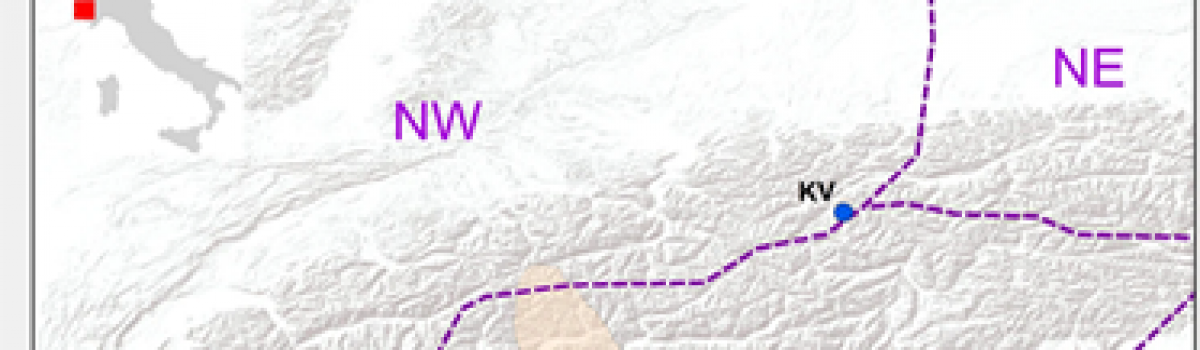
Location of Rio Martino Cave and of other sites mentioned in the text. Pink shadow indicates the area investigated in the synthesis on S Alps flood activity30; LS-Area of the cluster of deep-seated large scale landslides45; Ledro-Lake Ledro29; KV-Kauner Valley (tree-line elevation, Fig. 4);53 Rutor-Rutur mire (pollen percentage, Fig. 4)41;…

Devi effettuare l'accesso per postare un commento.